STRAMER
RECOVERING STRATEGIC METALS FROM LITHIUM-ION BATTERIES
THE PROPER MANAGEMENT OF LITHIUM-ION BATTERIES WILL BECOME AN ABSOLUTE NECESSITY IN THE SHORT TERM. Large companies in the sector are working on the creation of new recycling plants and battery treatment plants are being converted, complementing traditional batteries recycling with new lithiumion lines. Forecasts indicate a general increase in the use of these batteries, both in electric appliances and electric mobility. In fact, there is a need for recycling plants throughout the country including this new line of treatment.
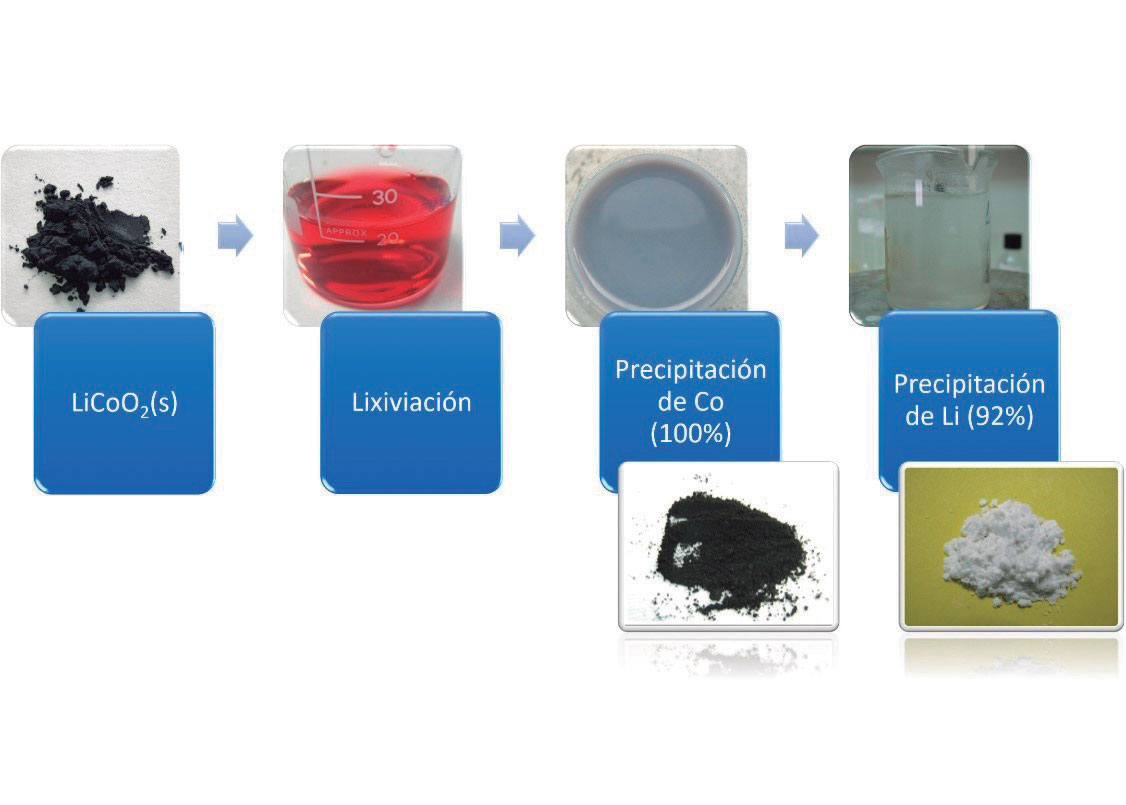
The waste management of lithium-ion batteries faces the challenge of introducing batteries into the recycling process, through Waste from Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) and battery management systems, as well as developing a valid method for the different types of batteries, especially LCO (LiCoO2) and NMC (LiNiMnCoO2). The most commonly used processes are mechanical, pyrometallurgical (discarded because the Li ends up in the slag), and hydrometallurgical, which are often combined.
REYDESA RECYCLING, a company of the Otua Group dedicated to the recovery of metals, leads STRAMER, where INATEC, the Otua Group’s R&D Unit, have also collaborated.

DRIVING FACTOR
 OBJECTIVES
OBJECTIVES
- Conduct a new production activity for the management of Li-ion batteries, for which analysing the stages that make up the process for recovering metals such as Li, Co and Ni is proposed.
- Minimise the environmental impact of treatment.
- Complete a study of industrial alternatives to current recovery.
 RESULTS
RESULTS
- In-depth technical knowledge has been obtained on energy storage systems from WEEE at the level of components present, quantities, separation methods and recycling possibilities.
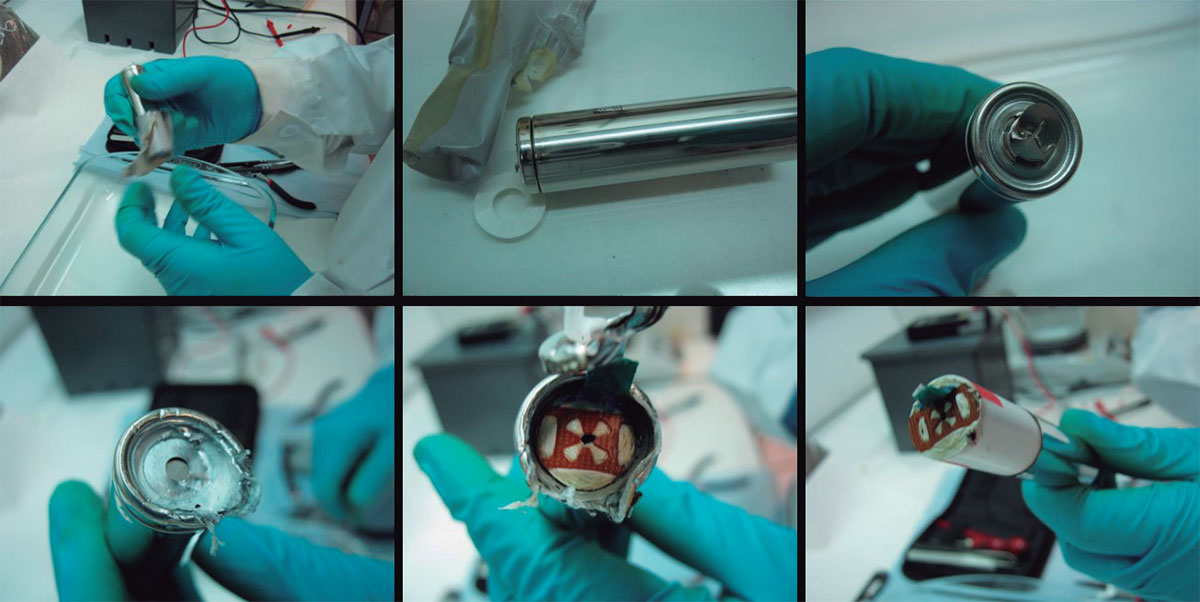
- A methodology for discharging and dismantling of Li-ion batteries, was developed, and a robust method for the recovery of the fractions of interest they contain: Cu, graphite, Al, stainless steel, polymers, and target metals: Li, Co and Ni.
- Drafting of a technology watch report on the industrial processes currently carried out by leading companies in the sector.
 CONCLUSIONS
CONCLUSIONS
- The analysis of various scenarios for the development of a new line of business has led to networking with companies to capture batteries.
- A continuation of STRAMER has been proposed to conduct a demonstration project of the developed process and implement improvements for its industrialisation.
ENVIRONMENTAL
TECHNICAL
ECONOMIC
COMMERCIAL
ON THE MARKET