RELOPA
FULL REUSE OF WASTE SLUDGE FROM THE PAPER INDUSTRY
From an environmental point of view, the treatment and recovery of sludge and paper waste is one of the major drawbacks of the paper industry. Currently 5% of the fibres are lost during the paper manufacturing process. This percentage represents thousands of tonnes of lost raw material, in addition to the generation of waste disposed of in landfills. Pulp and paper waste is the fourth largest waste stream in the Basque Country (182,000 tonnes generated in 2018) and is therefore one of the specific priority waste streams within the Basque Waste Prevention and Management Plan 2030.
ORLOGA is an engineering firm specialised in industrial scaling projects and is behind RELOPA, on which it has worked with ARALAR, a paper manufacturing company.

DRIVING FACTOR

 OBJECTIVES
OBJECTIVES
- Research, design and develop a new solution to obtain high quality nanocellulose from the recovery of waste sludge generated in the paper manufacturing process.
- Obtain and make high-performance nanocellulose available at a low production cost from the treatment of sludge from the paper industry.
- Treat and recover sludge from the ARALAR plant with a km 0 approach by using nanocellulose locally.
 RESULTS
RESULTS
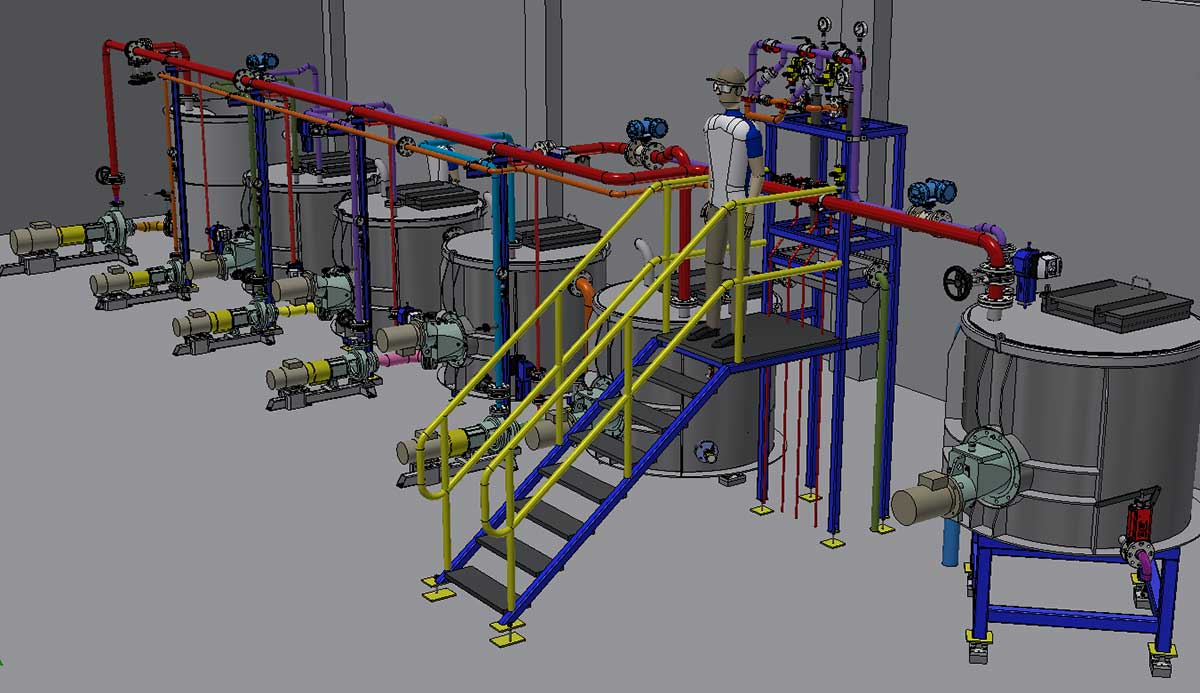
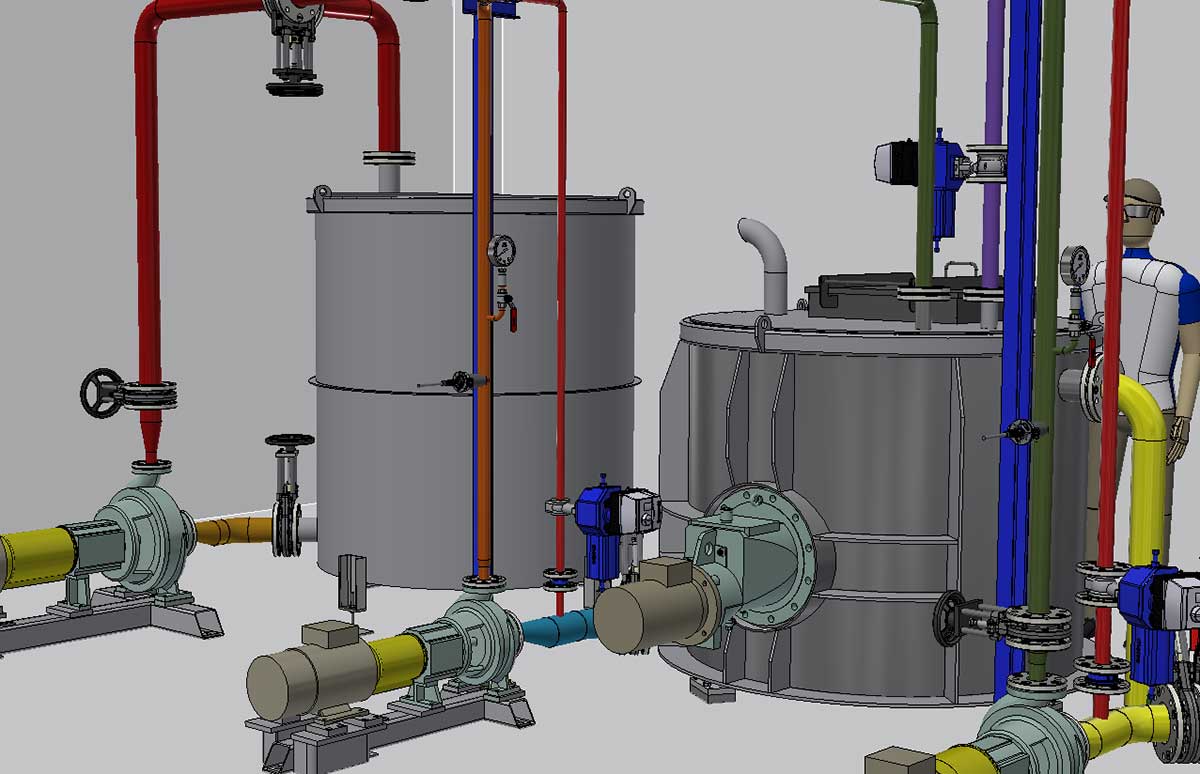
- Design and research two different processes at a pilot plant: (1) acid hydrolysis for the recovery of paper sludge (coloured and uncoloured) from the treatment plant; and (2) recovery of waste fibres by disintegration of the line prior to blending and sending to treatment.
- Design of a flexible modular plant to produce nanocellulose by acid hydrolysis of waste and virgin cellulose fibres, pending economic and environmental validation in a real environment.
- Creation of the B2B (Biomass to Biorefinery) start-up with the aim of developing, validating and launching the solution obtained on the market. Design of the B2B Roadmap, and presentation of an initial pilot plant project through HAZI in Enkarterri.
 CONCLUSIONS
CONCLUSIONS
- The local approach to the use of nanocellulose in the plant where it is manufactured from its waste is a priority for a viable implementation from the economic, environmental, legal and market point of view.
- It is necessary to validate the results obtained in a real environment through the implementation of a flexible modular plant that enables us to carry out the necessary verifications and validations in order to implement the system in different types of customers.
- This validation will enable industrial applications of nanocellulose to be scaled up in different sectors by carrying out demonstration R&D&I projects with companies and technology centres.
ENVIRONMENTAL
TECHNICAL
ECONOMIC
COMMERCIAL
ON THE MARKET