IMACERFA
CERTIFICATION AND USE OF MATERIALS FOR ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING OF AERONAUTICAL COMPONENTS
THE AERONAUTICAL SECTOR ACCOUNTS FOR AROUND 3% OF GLOBAL CO2 EMISSIONS. One of the ways to curb emissions in the sector is reducing aircraft weight. Additive manufacturing (AM) technology can achieve lighter aircraft, but it also requires materials to be certified based on the requirements of the aeronautical industry. MIZAR, a leading AM company, has observed that clear success cases have failed due to a lack of quality documentation of manufacturing processes. This project deals with the certification of different materials with high expectations in aeronautical applications, and MIZAR has relied on EOS and STRATASYS, companies specialising in 3D printing, and the GAIKER Technology Centre, for its execution.

 OBJECTIVES
OBJECTIVES
- Include MIZAR in the portfolio of aeronautical companies’ suppliers, as a leader in additive manufacturing processes in the sector.
- Certify two specific materials: PEKK+CF and Nylon+CF, to produce aircraft components with additive manufacturing processes.
- Develop the manufacturing process of metallic materials in DMLS (Direct Metal Laser Sintering) with variable layer thickness for aeronautical certification.
- Characterise titanium alloys in EBM (Electron Beam Melting) technologies to be used in topology optimisation in the aeronautical sector.
 RESULTS
RESULTS
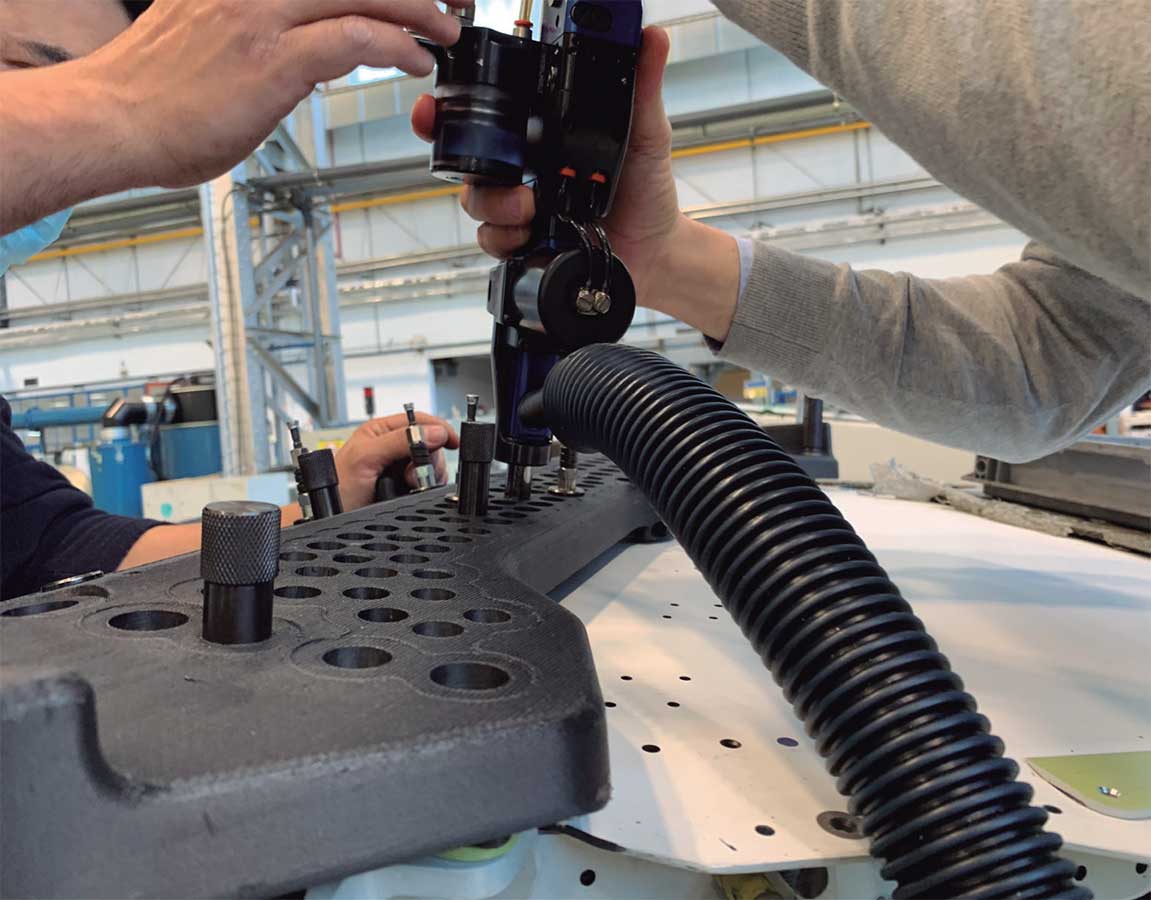
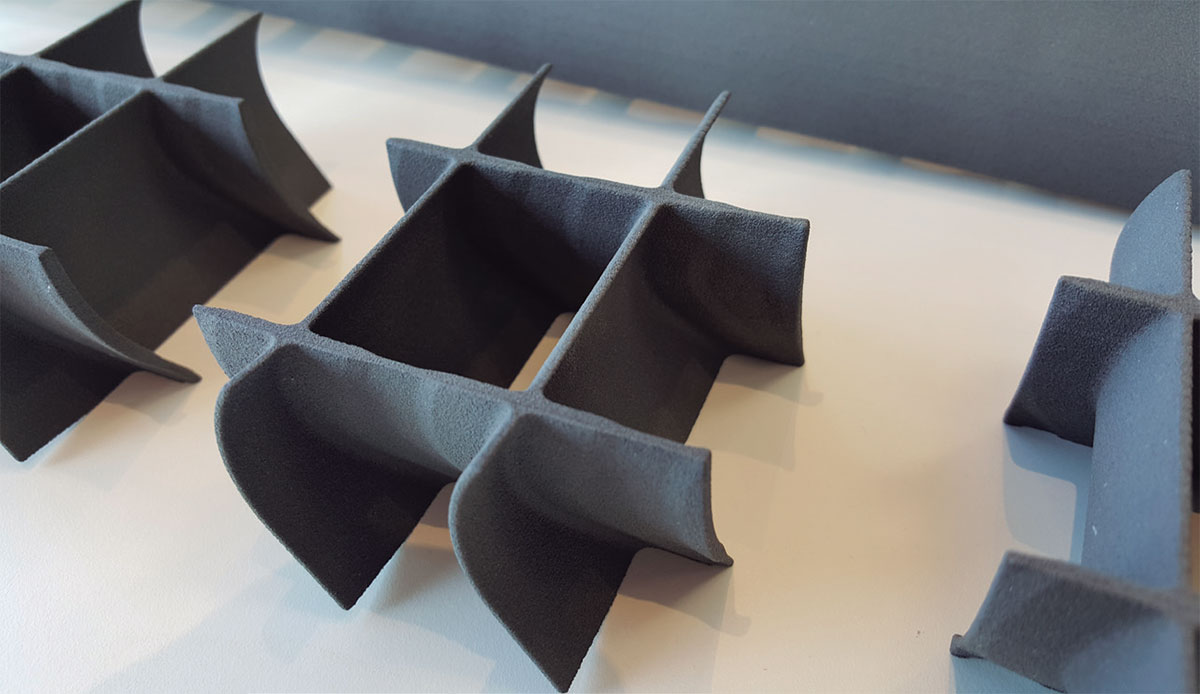
- Improved dimensional tolerances of flat drilling jigs made with Nylon+CF and production of curved drilling jigs being tested on aircraft.
- Simultaneous production of parts of different thickness in DMLS.
- 44.7% weight reduction of aircraft fittings through AM.
- MIZAR was invited by Airbus Defence & Space to produce an application note describing the developed application, which is available at the following link https://mizaradditive.com/en/aerospace-additive-manufacturing/
 CONCLUSIONS
CONCLUSIONS
- The production of curved Nylon+CF sections is a technically challenging process, which has been successfully achieved and is currently being tested on the market.
- Relevant in-house know-how has been developed working with parts with less than standard layer thickness in DMLS, with the possibility of working on several thickness simultaneously, resulting in interesting added cost savings.
- The certifi cationprocess of materials for the aeronautical sector requires technical solutions and continuous approval work with corporate clients. Input from the value chain, including Airbus in this case, is mandatory.
ENVIRONMENTAL
TECHNICAL
ECONOMIC
COMMERCIAL
ON THE MARKET