HEAT IT YOURSELF FOR SUSTAINABILITY. CIRCULARITY IN ENERGY-INTENSIVE INDUSTRIES
Generating new knowledge and innovation about the use and life cycle of materials and energy, identifying specific areas of action to increase material productivity, adopting innovative solutions and promoting resource savings and waste reduction are direct objectives of the transformative project on "Circularity in value chains" included in the 2030 Environmental Framework Programme for the Basque Country.
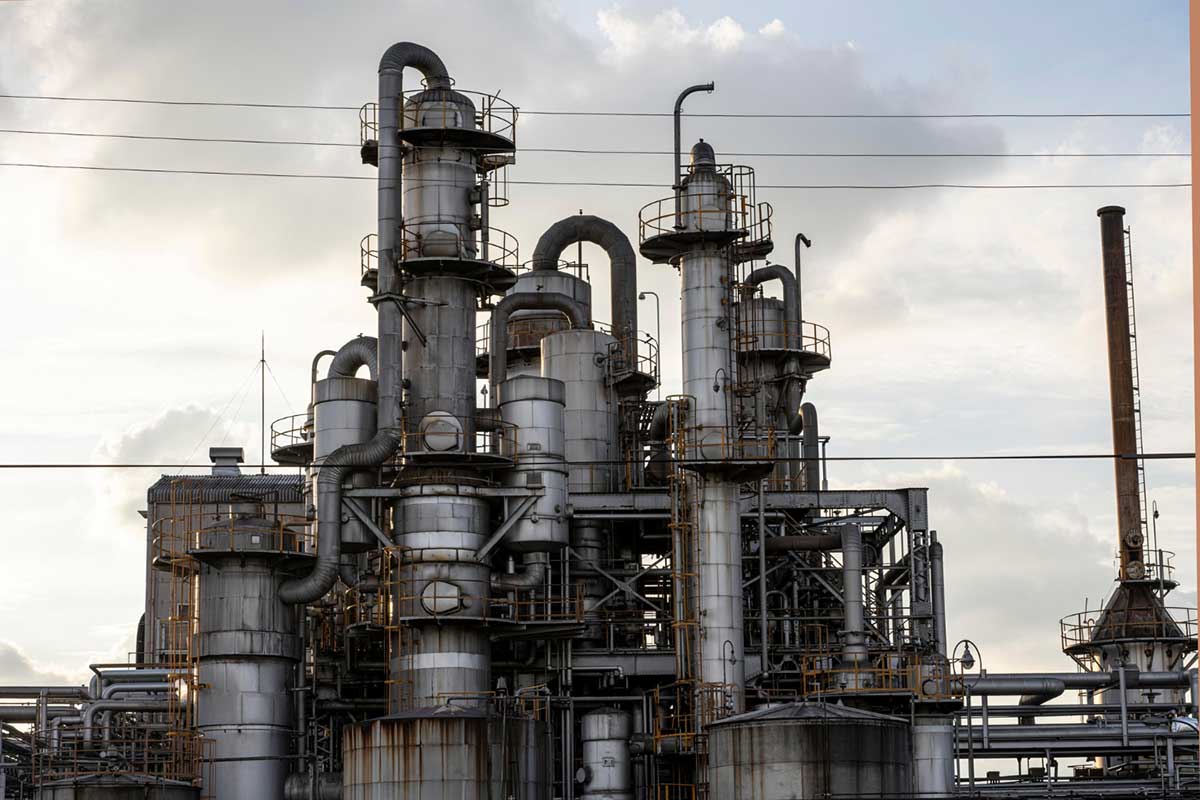
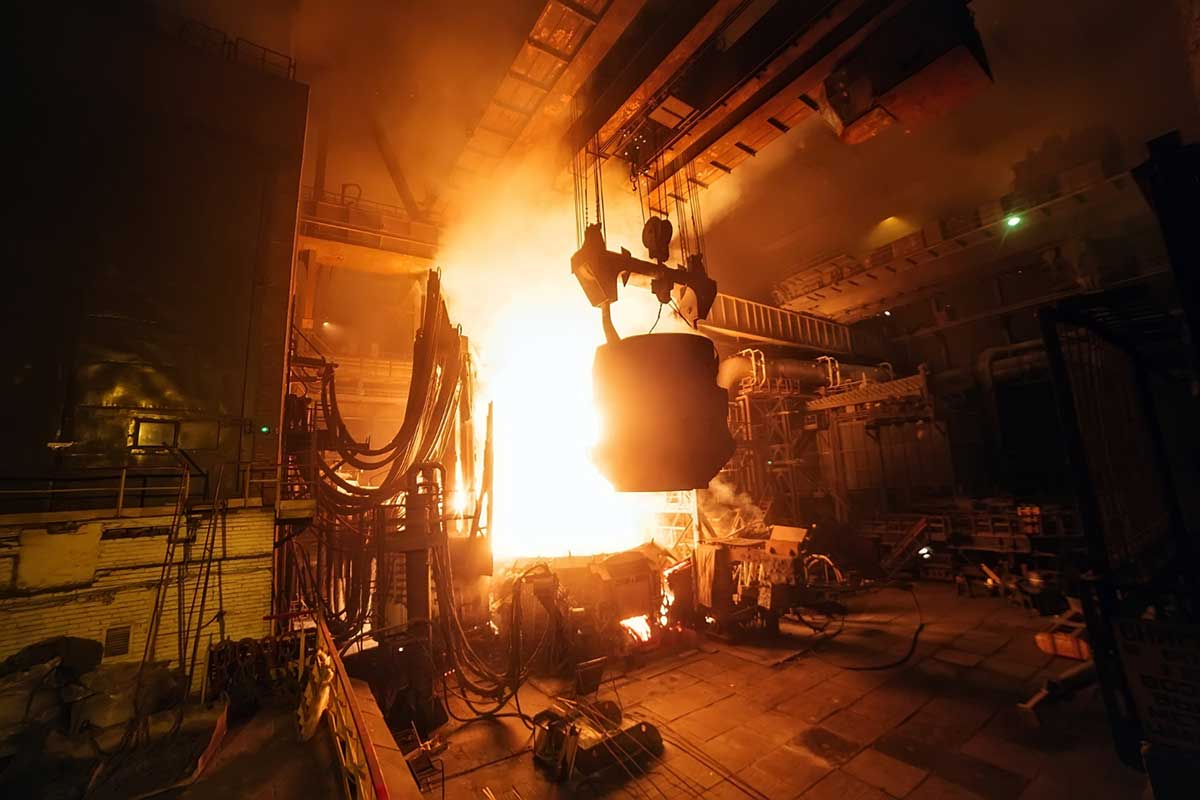
Most energy-intensive industries use energy in the form of heat and, once the process heat has been applied, the exhaust gases are discharged into the atmosphere via chimneys. The waste heat contained in these exhaust gases is the largest heat loss at manufacturing plants. Most industries using the Electric Arc Furnace lower the temperature and remove the contamination from the large amount of hot gases produced before releasing them into the atmosphere. Therefore, not only is the heat of the gases wasted, but also energy is consumed to treat them and lower their temperature before releasing them.
Waste heat recovery in industrial processes is a well-known topic, but only low/medium temperature solutions under "clean" conditions can be considered mature for widespread implementation. Hot streams containing harmful chemicals or condensible particles require more costly equipment and present fouling, degradation or contamination problems, and therefore require further research and implementation efforts to extract their full energy potential and to be cost-effective.













 Project website
Project website